11. 感知器算法
感知器算法
掌握了感知器技巧后,我们就可以编写完整的感知器运算的算法了!
下面的视频将介绍感知器算法的伪代码,现在你还不需要担心什么是学习速率(learning rate),我们在之后的课程中会详细介绍为什么这里的伪代码中有学习率。
在视频下面的测验中,你将有机会用 Python 将其编成代码,并看看自己的感知器分类成果。加油!
DL 12 Perceptron Agorithm Pseudocode (1)
编写感知器算法
该编写代码了!在此练习中,你将实现感知器算法以分类下面的数据(位于文件 data.csv 中)。
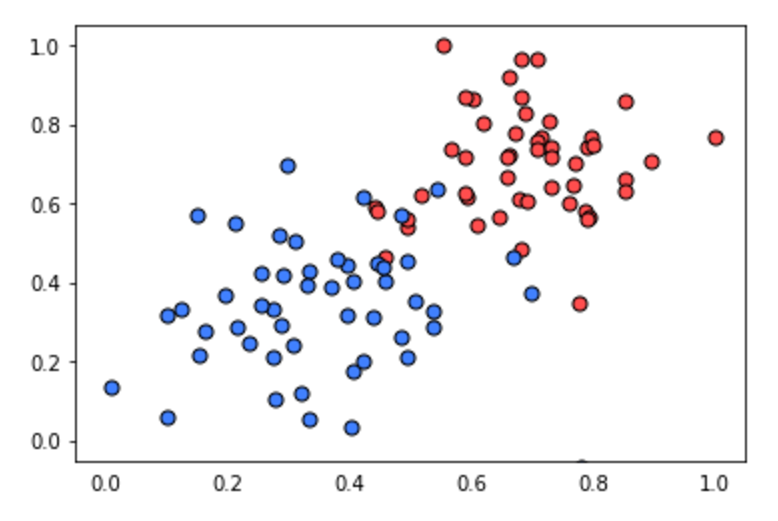
感知器步骤如下所示。对于坐标轴为
(p,q)
的点,标签 y,以及等式
\hat{y} = step(w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + b) 给出的预测
- 如果点分类正确,则什么也不做。
- 如果点分类为正,但是标签为负,则分别减去
\alpha p, \alpha q,
和
\alpha
至
w_1, w_2,
和
b - 如果点分类为负,但是标签为正,则分别将
\alpha p, \alpha q,
和
\alpha
加到
w_1, w_2,
和
b
上。
然后点击测试运行绘出感知器算法给出的解决方案。它实际上会画出一组虚线,显示算法如何接近最佳解决方案(用黑色实线表示)。
请随意改动算法的参数(epoch 数量、学习速率,甚至随机化初始参数),看看初始条件对解决方案有何影响!
Start Quiz: